Moiré Patterns in 2D Materials
This research explores moiré patterns in two-dimensional superlattices, focusing on the manipulation of these patterns by applying mechanical stress to graphene and hBN layers.
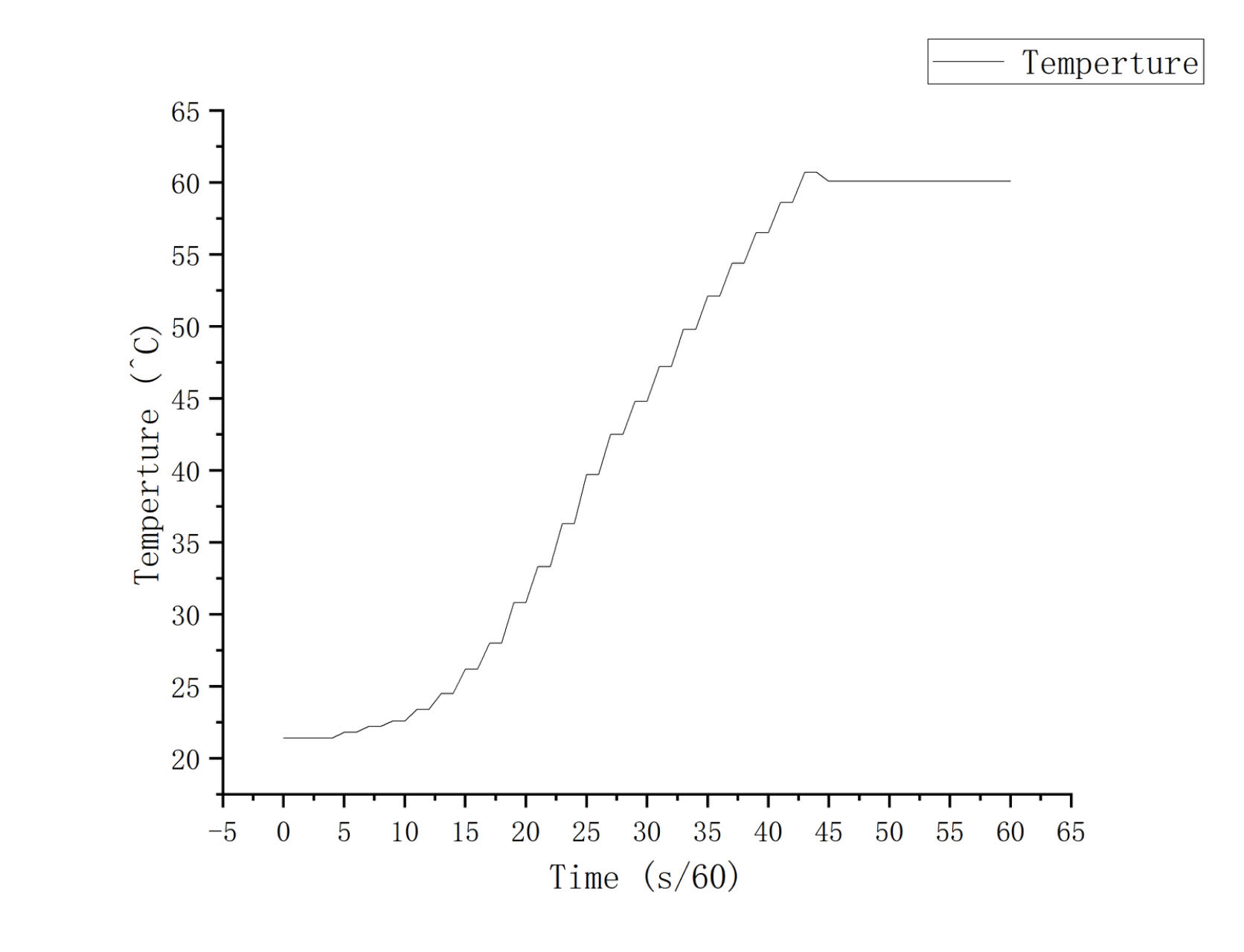
We used atomic force microscopy (AFM) to find 42nm and 24nm thick hexagonal boron nitride(hBN) that could be used as the bottom hBN and Mid-hBN. Next, We have found some graphene that appears to have the Lattice orientation in the same direction as Mid-hBN and the right shape under optical microscopy. After finding all suitable samples, we successfully stacked them together on a Si/Sio2 substrate. Afterwards, in order to apply stress to change the shape of the moire, we successfully transferred it to a plastic substrate and successfully applied stress through PMMA.
I utilized DesignCAD to design the electrodes. Following the design phase, I employed electron beam evaporation to deposit a thin metal film on the sample's surface. The samples were then exposed under a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Through a series of repeated operations including development and etching, I successfully grew the alignment marks and electrodes. This process was further refined through Plasma etching to complete the sample processing. Finally, the prepared sample was installed into a cryogenic strong magnetic device for further experiments.
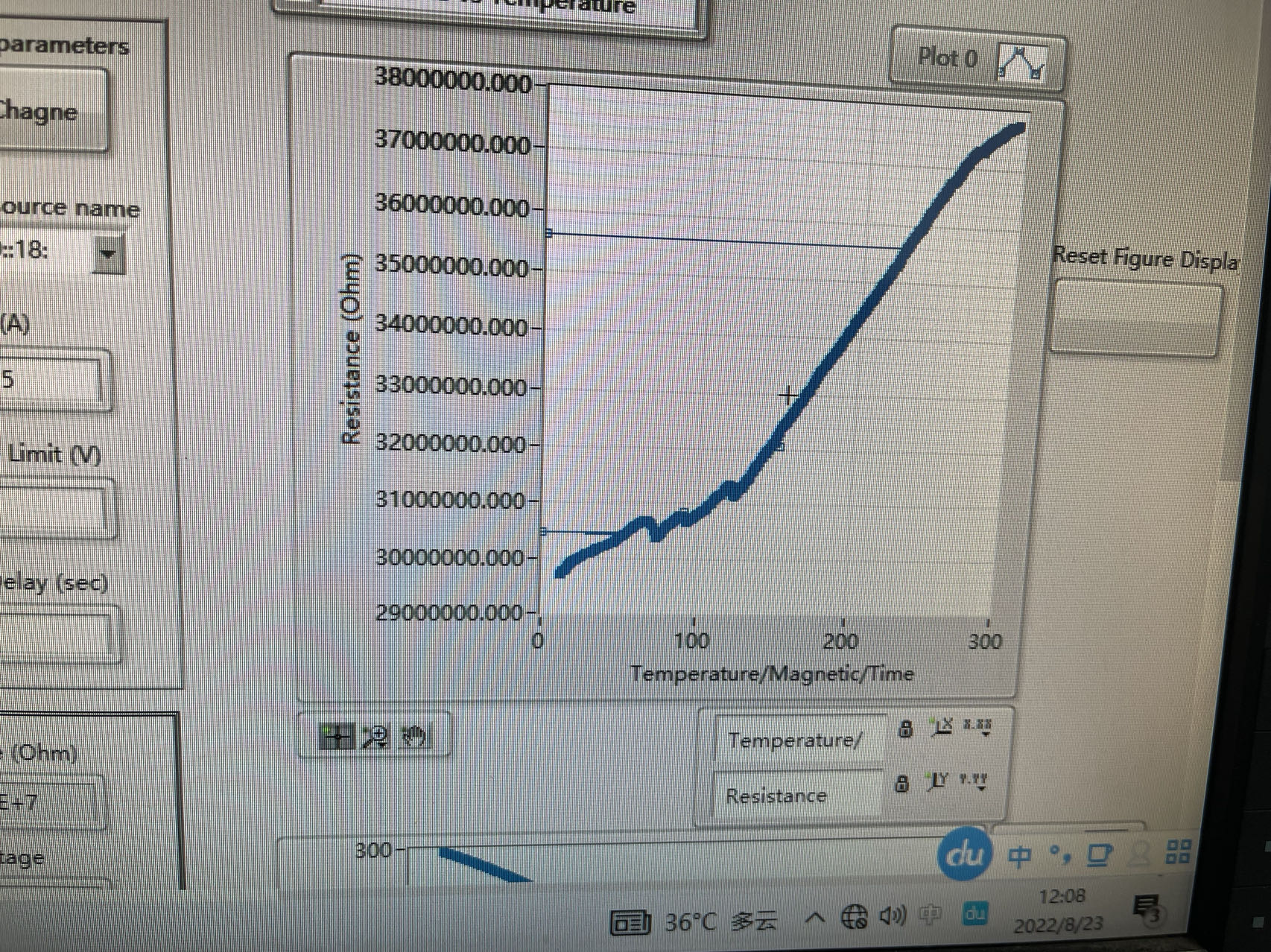
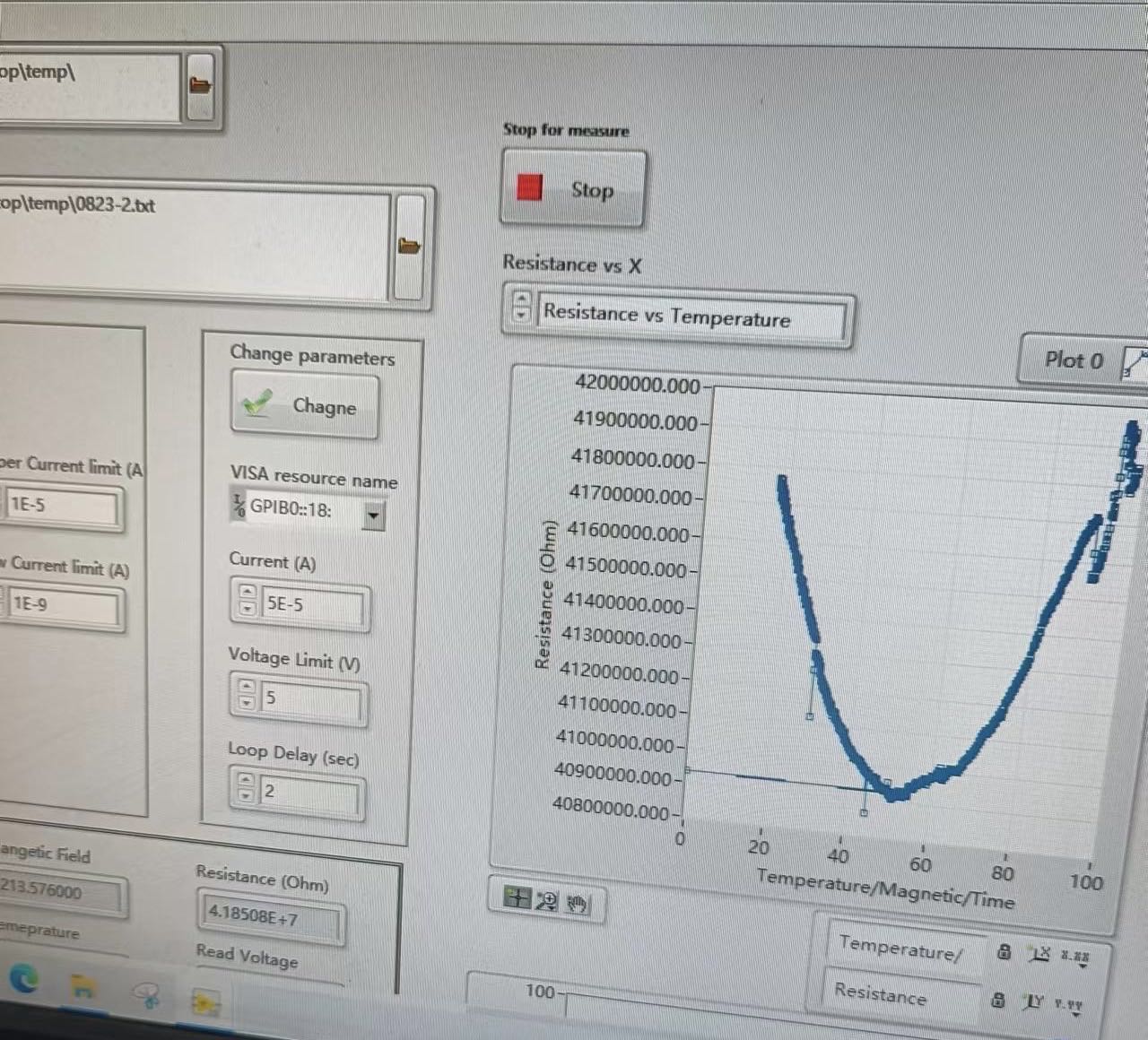
The change and distribution of resistance and current density under different magnetic field intensity were measured at 4K temperature. We can clearly see the split of the Landau level and the secondary Dirac points. That means we've managed to find and change the size and shape of moire.
At present, the shape and size of moire have been successfully changed by applying stress under the condition of 4K strong magnetic field, and the changes of its resistance and current density have been tested. It is proved that the scheme of changing the shape of moire by applying stress to PMMA is feasible.
This research explores moiré patterns in two-dimensional superlattices, focusing on the manipulation of these patterns by applying mechanical stress to graphene and hBN layers.
Download Moiré Poster (PDF)
Research Presentation
Research Presentation 2
Time: July 10, 2023 - Present
Professor: Xu Du
Place: Stony Brook University, Department of Physics and Astronomy